Spring Cloud Configとは
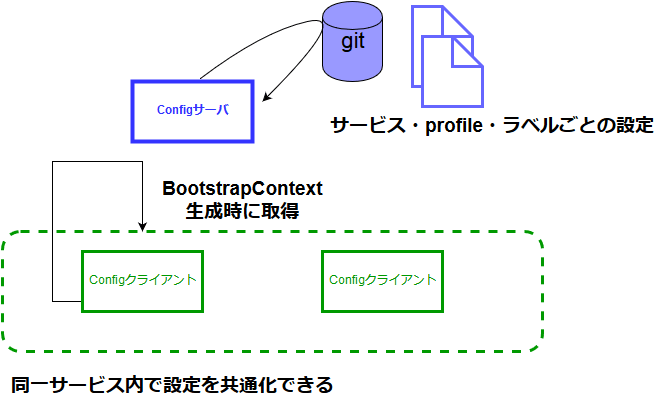
複数アプリケーション(同一サービス)間で共通の設定を提供するプロダクト。
クライアント-サーバ型のアーキテクチャ。
- Configサーバ(githubやファイルシステム上のgitリポジトリから設定を取得してクライアントに配布する)
- Configクライアント(サーバに要求して設定を取得する)
何がいいの?
- 複数アプリケーション(同一サービス)間の設定の不一致を避けられる。
- 再起動なしで設定を再配布できる。
サンプル書いた
- https://github.com/kimullaa/config-server
- https://github.com/kimullaa/config-client
- https://github.com/kimullaa/spring-cloud-config-repo
実装方法
Configサーバ
pom.xmlで必要なjarを指定する。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
@EnableConfigServerをつける。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class ConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
クライアントに配布する設定ファイルの配置場所をapplication.propertiesで指定する。portは8888が一般的っぽい。
server.port = 8888
spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri = https://github.com/kimullaa/spring-cloud-config-repo.git
githubでもローカルのファイルシステム上にあるgitリポジトリでもok。publicでもprivateなリポジトリでもok。sshでもok。特に制約なし。
リポジトリはアプリごとに1つ用意するのがシンプルでよい。
ファイル名は{app名}-{profile}にする。
https://github.com/kimullaa/spring-cloud-config-repo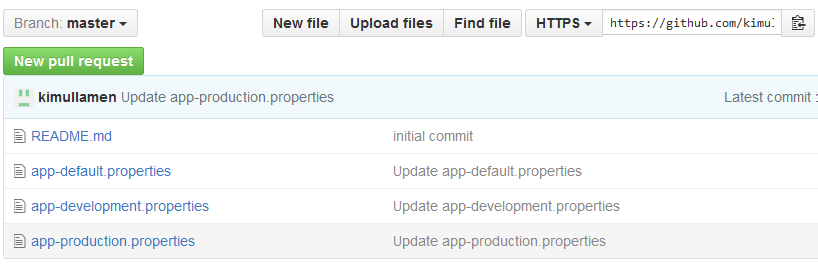
Configサーバといっても、以下のようなエンドポイントを持ったAPサーバ。
(labelはdefaultがmasterで省略可能)
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{application}-{profile}.properties
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties
そのため、curlで設定を確認できる。
$ curl -X GET http://localhost:8888/app/production
{
"name":"app",
"profiles":[
"production"
],
"label":null,
"version":"1469d0351becdfcc a1bffa98f4a07ee685af8255",
"propertySources":[
{
"name":"https://github.com/kimulla men/spring-cloud-config-repo.git/app-production.properties",
"source":{
"greeting":"production"
}
}
]
}
$ curl -X GET http://localhost:8888/app-development.properties
greeting: development
Configクライアント
pom.xmlで必要なjarを指定する。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
bootstrap.propertiesにconfigサーバのURIを指定する。
spring.cloud.config.uri = http://localhost:8888
spring.application.name = app
spring.profiles.active = production
bootstrap.propertiesはBootstrapContext※を生成するときに利用するファイル。
Configサーバから取得した設定内容を読み込んだクラスが生成される。
※BootstrapContextはApplicationContextの子親コンテキスト。詳細はリファレンスを参照する。
設定を取得できてるか確認するためのControllerを実装する。
@Valueでpropertiesファイルの値を取得できる。(:not-foundは見つからなかったときのデフォルト値)
@RestController
public class GreetingRestController {
@RequestMapping("/greeting")
public String greeting(@Value("${greeting:not-found}") String greeting) {
return greeting;
}
}
クライアントから見たときのファイル名とアプリの関連性は?
{app名}-{profile}-{label}.properties
| app名 | spring.application.name |
| profile | spring.active.profiles |
| label | gitのbranch名(デフォルトmaster) |
設定変更の反映
いくらgitのファイルを更新しても、アプリ側が設定ファイルを再度読み込むまでは値が反映されない。設定ファイルを再度読み込むためには、/refreshエンドポイントにPOSTすればよい。
細かい理由
- @ConfigurationPropertiesアノテーションが付与されているクラスは@RefreshScopeになる
- @RefreshScopeのBeanは/refreshエンドポイントにPOSTするとBeanが再生成される
- ConfigClientAutoConfigurationクラス内でConfigServicePropertySourceLocatorという設定ファイル読み込み用のクラスが@RefreshScopeになっているため/refreshエンドポイントにPOSTすれば更新されるっぽい
$ curl -X POST localhost:8080/refresh
["greeting"]
でも全部のConfigクライアントに/refreshなんてしたくない
Spring Cloud Busというプロダクトを使えば、Configクライアントから他のConfigクライアントへ更新通知を伝搬できるようになる。~~また今度調べる。~~調べた。
SpringCloudBusで簡単にConfigの更新をアプリにブロードキャストする - SIerだけど技術やりたいブログkimulla.hatenablog.com