課題
SpringSecurityのサンプルでは、以下のようにROLEに基づいて認可していることが多い。
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception {
httpSecurity.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
が、ロールに基づいた認可ではなく権限に基づいた認可を行いたい。つまり、ロールごとに複数の権限を持たせ、ユーザにロールを複数割り当てたい。
参考 業務システムにおけるロールベースアクセス制御
解決方法
SpringSecurityでは、AuthenticationクラスをもとにアクセスコントロールするためのEL式が提供されている。 ログイン時にAuthenticationクラスのauthoritiesに権限情報を設定し、EL式を利用すれば権限に基づいた認可が実現できる。
参考 Spring Security 使い方メモ 認証・認可
参考 TERASOLUNA Server Framework for Java (5.x)
Expression Description hasRole([role]) Returns true if the current principal has the specified role. By default if the supplied role does not start with ‘ROLE_’ it will be added. This can be customized by modifying the defaultRolePrefix on DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler. hasAuthority([authority]) Returns true if the current principal has the specified authority permitAll Always evaluates to true isAuthenticated() Returns true if the user is not anonymous … …
参考 27.1.1 Common Built-In Expressions
上記EL式の実装クラスは、SecurityExpressionRoot。 参考 SecurityExpressionRoot
hasRoleとhasAuthorityの違いは、権限の文字列に”ROLE_“プレフィックスをつけてくれるか、つけてくれないか。hasRoleのプレフィックスはROLE以外も指定できるため、同じふるまいにもできる。つまり、hasRoleという名前でおもいっきりロールを意識させられているが、実際にはロールじゃなくてもいい。ただのGrantedAuthorityの文字列のチェックでしかない。 が、名前がまぎらわしいので、権限に基づいた認可をする場合はhasAuthorityを利用したほうが無難だと思う。
実装例
ソースコード全体はgithubに上げました。
実装したアプリ。
- ロールは、『管理者』と『一般』の2つ
- 権限は、『権限管理』と『ユーザ一覧表示』の2つ
シナリオ
- 一般ユーザでログインし、『権限管理』を参照できないことを確認する
- 管理者ユーザでログインし、一般ユーザに『権限管理』の権限を与える
- 一般ユーザでログインしなおし、『権限管理』を参照できることを確認する
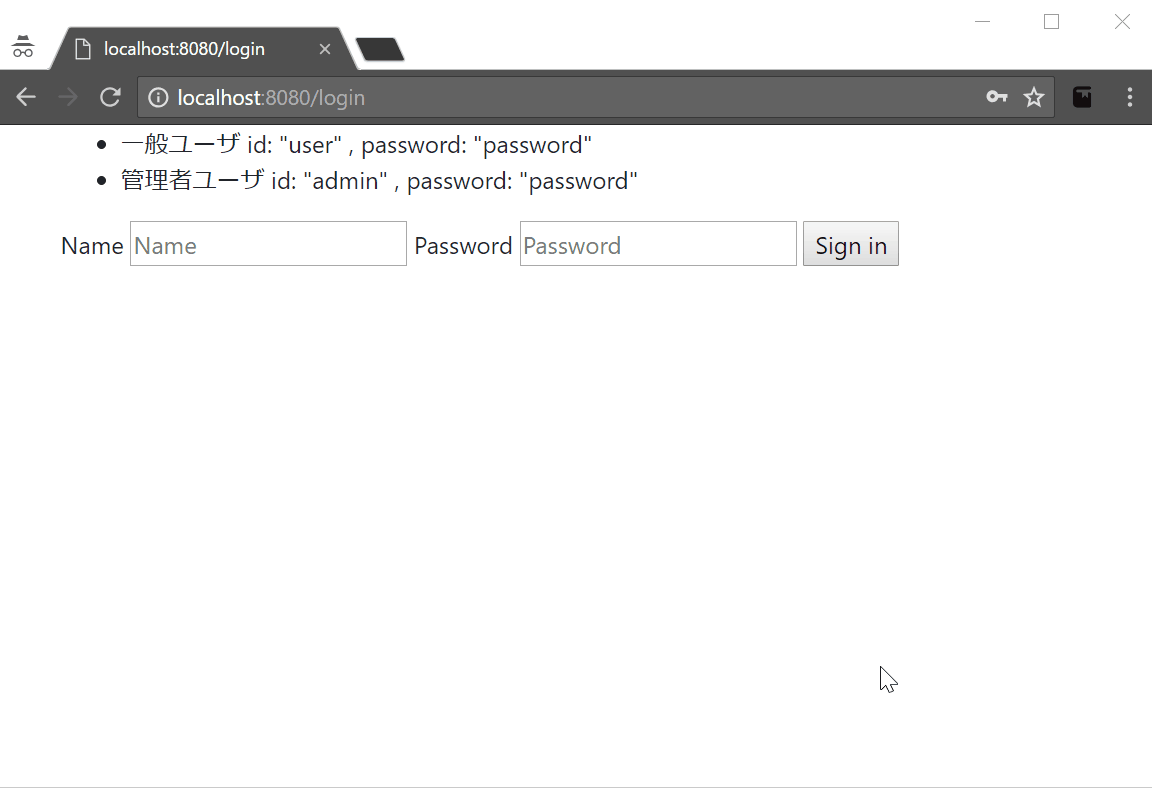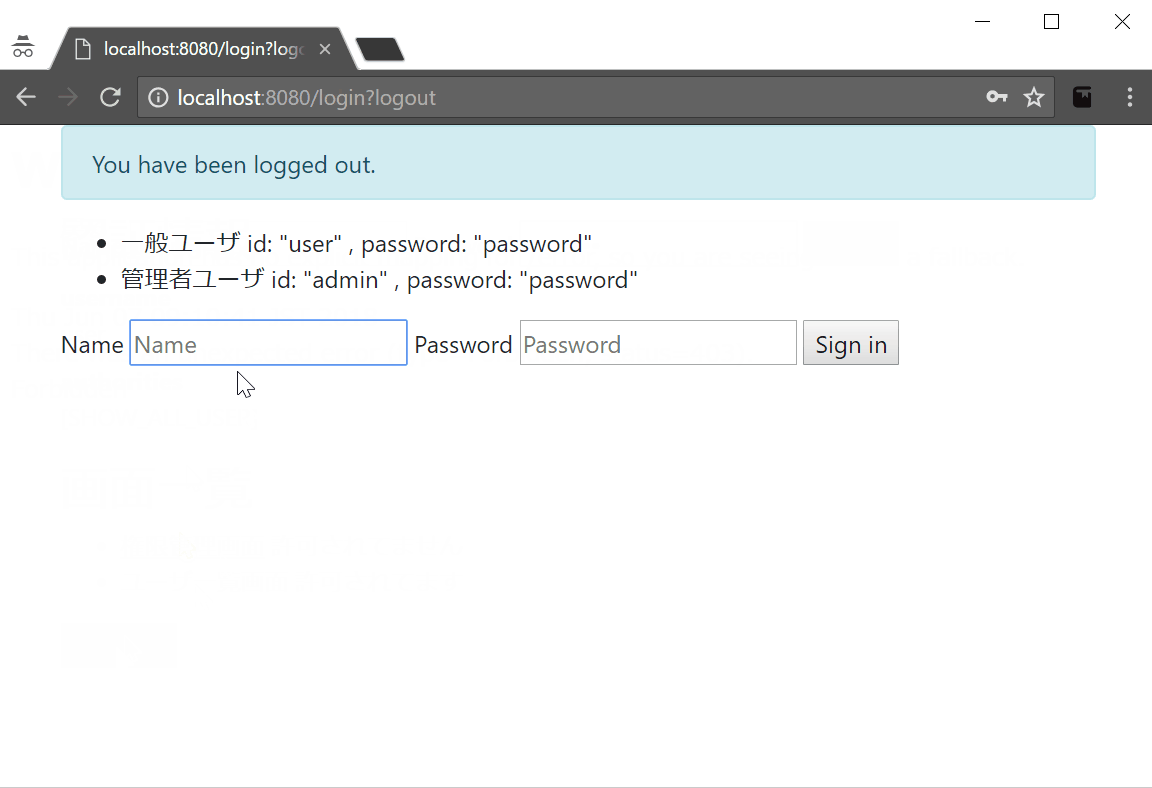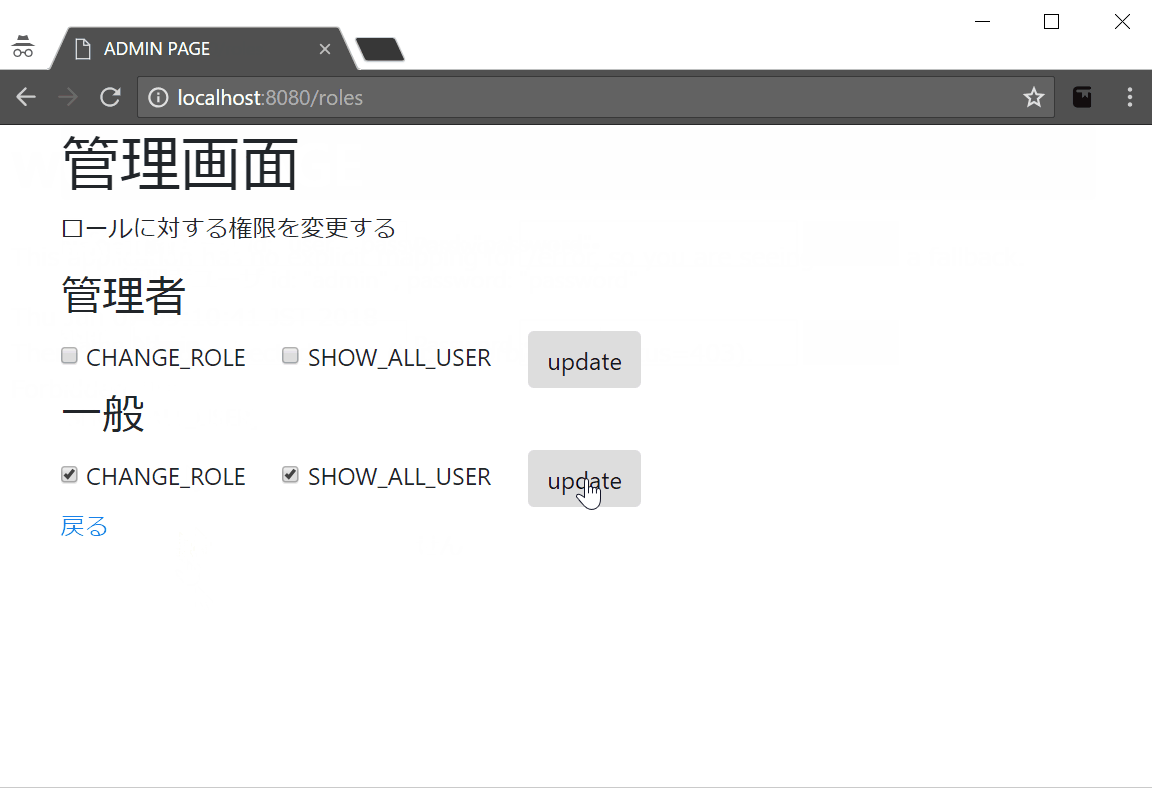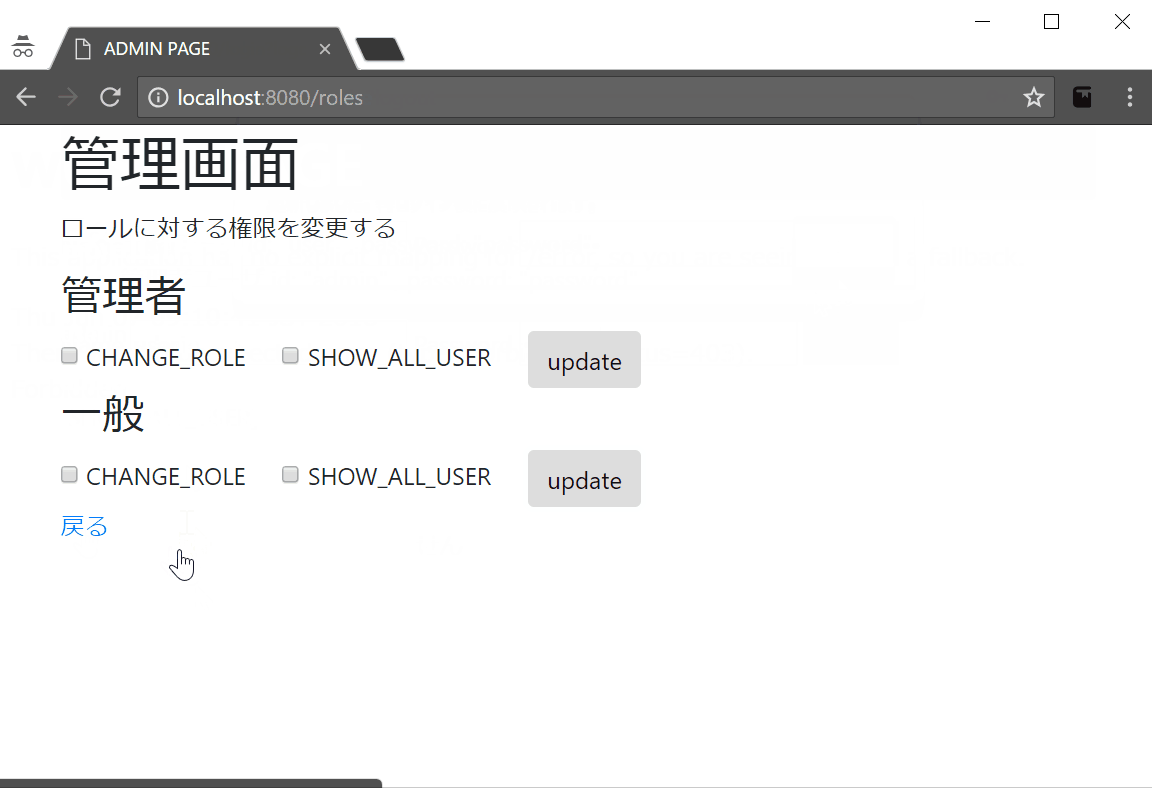
Userは複数のRoleを保持する。
@Data
@Entity
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String password;
@ManyToMany
private List<Role> roles;
public User(String name, String password, List<Role> roles) {
this.name = name;
this.password = password;
this.roles = roles;
}
}
Roleは複数のPermissionを保持する。
@Data
@Entity
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Role implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
@ManyToMany
private List<Permission> permissions;
public Role(String name, List<Permission> permissions) {
this.name = name;
this.permissions = permissions;
}
public Role(Long id, List<Permission> permissions) {
this.id = id;
this.permissions = permissions;
}
@Data
@Entity
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Permission implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
public Permission(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Permission(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
ユーザ情報の取得処理で、UserDetailsのGrantedAuthorityに権限を設定する。
CustomUserDetailsService.java
@Service
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User target = userRepository.findOneByName(username);
List<SimpleGrantedAuthority> authorities = target.getRoles().stream()
.flatMap(i -> i.getPermissions().stream())
.map(i -> new SimpleGrantedAuthority(i.getName()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User user = new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(target.getName(), target.getPassword(), authorities);
return user;
}
}
あとは、権限に基づいて認可の設定をするだけ。
WebSecurityConfig.java
@EnableWebSecurity
@AllArgsConstructor
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
...
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception {
httpSecurity.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.mvcMatchers(HttpMethod.PUT,"/api/roles/*").hasAuthority("CHANGE_ROLE")
.mvcMatchers("/roles").hasAuthority("CHANGE_ROLE")
.mvcMatchers("/users").hasAuthority("SHOW_ALL_USER")
...
}
...