課題
Springには、非同期に処理を実行するための@Asyncアノテーションがある。
参考 7. Task Execution and Scheduling
Spring @Asyncで非同期処理をするときの注意点 - SIerだけど技術やりたいブログwww.kimullaa.com
デフォルトだとスレッド管理(TaskExecutor)にSimpleAsyncTaskExecutorが使われる。 このクラスは@Asyncの呼び出しごとにスレッドを生成し、またデフォルトでは、スレッド数の制限がない。
TaskExecutor implementation that fires up a new Thread for each task, executing it asynchronously. Supports limiting concurrent threads through the “concurrencyLimit” bean property. By default, the number of concurrent threads is unlimited.
NOTE: This implementation does not reuse threads! Consider a thread-pooling TaskExecutor implementation instead, in particular for executing a large number of short-lived tasks. 参考 SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor Javadoc
@Asyncの同時実行数を絞りたい。また、スレッドを再利用したい。
解決方法
TaskExecutorにThreadPoolTaskExecutorを使用する。
参考 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor Javadoc
ThreadPoolTaskExecutorはjava標準のThreadPoolExecutorをラップしたクラス。
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor This implementation is the most commonly used one. It exposes bean properties for configuring a java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor and wraps it in a TaskExecutor. If you need to adapt to a different kind of java.util.concurrent.Executor, it is recommended that you use a ConcurrentTaskExecutor instead.
ThreadPoolExecutorはパラメータで以下の設定ができる。
パラメータ: corePoolSize - アイドルであってもプール内に維持されるスレッドの数 maximumPoolSize - プール内で可能なスレッドの最大数 keepAliveTime - スレッドの数がコアよりも多い場合、これは超過したアイドル状態のスレッドが新しいタスクを待機してから終了するまでの最大時間 unit - keepAliveTime 引数の時間単位 workQueue - タスクが超過するまで保持するために使用するキュー。このキューは、execute メソッドで送信された Runnable タスクだけを保持する
また、スレッドの生成ルールに関する記述は以下のとおりで、maximumPoolSizeに同時実行数を指定すれば、最大同時実行数が制御できる。ただし、キューがいっぱいにならないとcorePoolSize からmaximumPoolSizeまでスレッドが生成されない。
参考 stack overflow
コアおよび最大プールサイズ corePoolSize (getCorePoolSize() を参照) と maximumPoolSize (getMaximumPoolSize() を参照) で設定された境界に従って、ThreadPoolExecutor は自動的にプールサイズを調整します (getPoolSize() を参照)。新しいタスクが execute(java.lang.Runnable) メソッドで送信され、corePoolSize よりも少ない数のスレッドが実行中である場合は、その他のワークスレッドがアイドル状態であっても、要求を処理するために新しいスレッドが作成されます。corePoolSize よりも多く、maximumPoolSize よりも少ない数のスレッドが実行中である場合、新しいスレッドが作成されるのはキューがいっぱいである場合だけです。corePoolSize と maximumPoolSize を同じ値に設定すると、固定サイズのスレッドプールが作成されます。maximumPoolSize を Integer.MAX_VALUE などの実質的にアンバウンド形式である値に設定すると、プールに任意の数の並行タスクを格納することができます。
ThreadPoolExecutorに設定することで、上記をコントロールする。
検証
pom.xml
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
taskExecutorを生成し、@QualifierでBeanに名前をつける。(TaskExecutorがひとつだけなら@Qualifierは不要)
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class AsyncApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AsyncApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
@Qualifier("heavyTaskTaskExecutor")
public TaskExecutor taskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(1);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(2);
executor.setQueueCapacity(2);
return executor;
}
}
非同期にしたい処理に@Asyncアノテーションをつける。 また、名前をつけたTaskExecutorを利用するために@Asyncアノテーションの引数に指定する。
@Slf4j
@Service
public class TaskServiceImpl implements TaskService {
@Async("heavyTaskTaskExecutor")
@Override
public void heavyTask() {
try {
log.info("start heavy task");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
log.info("end heavy task");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
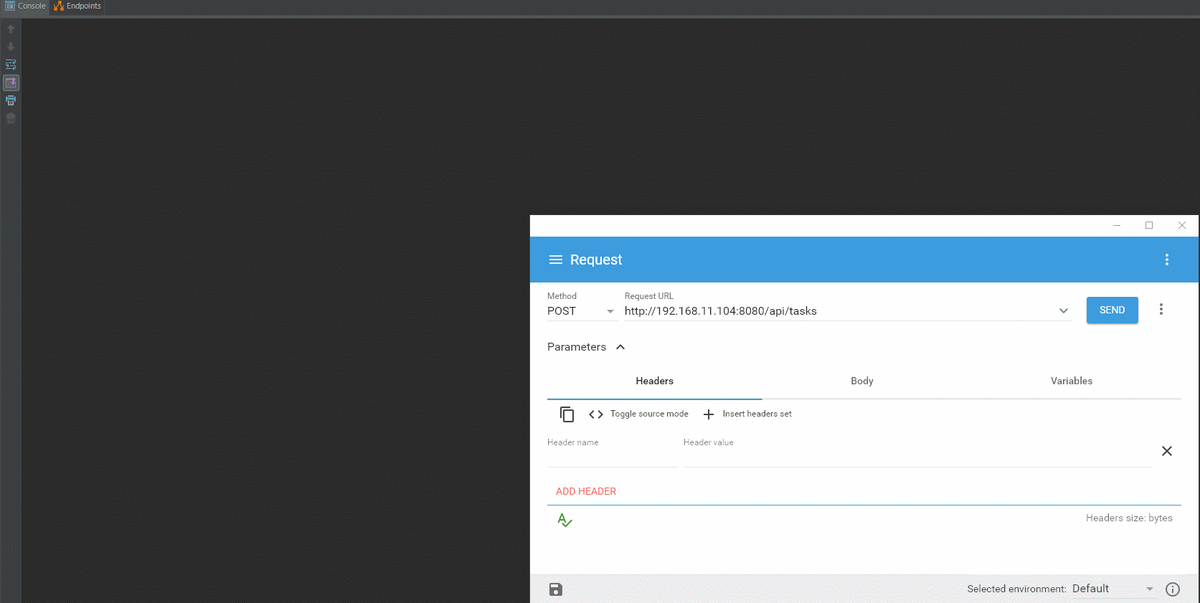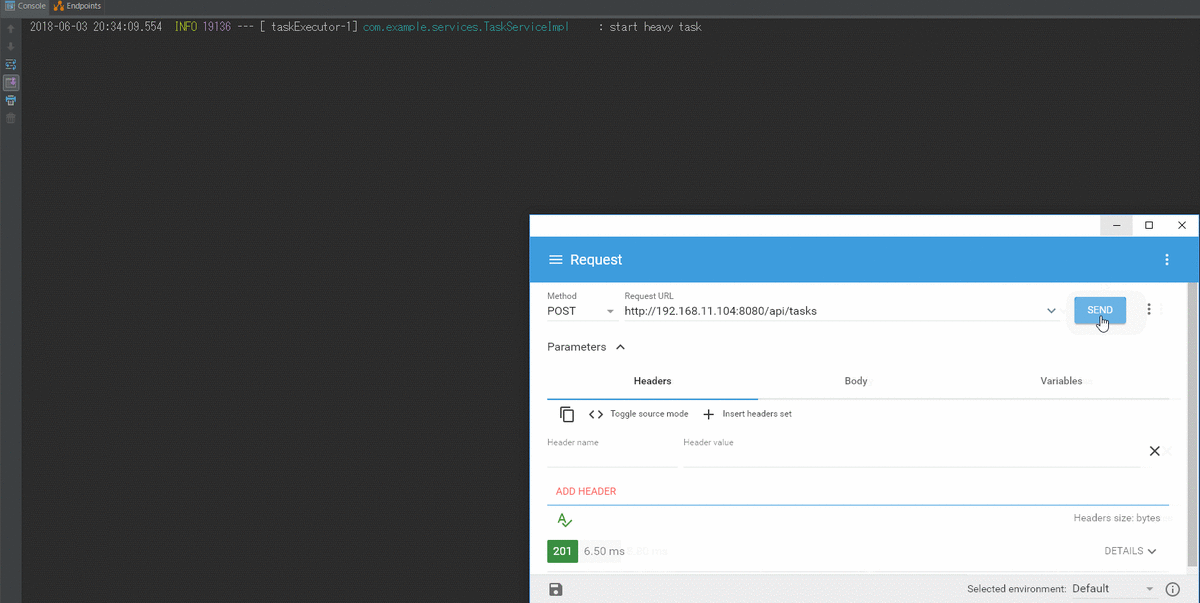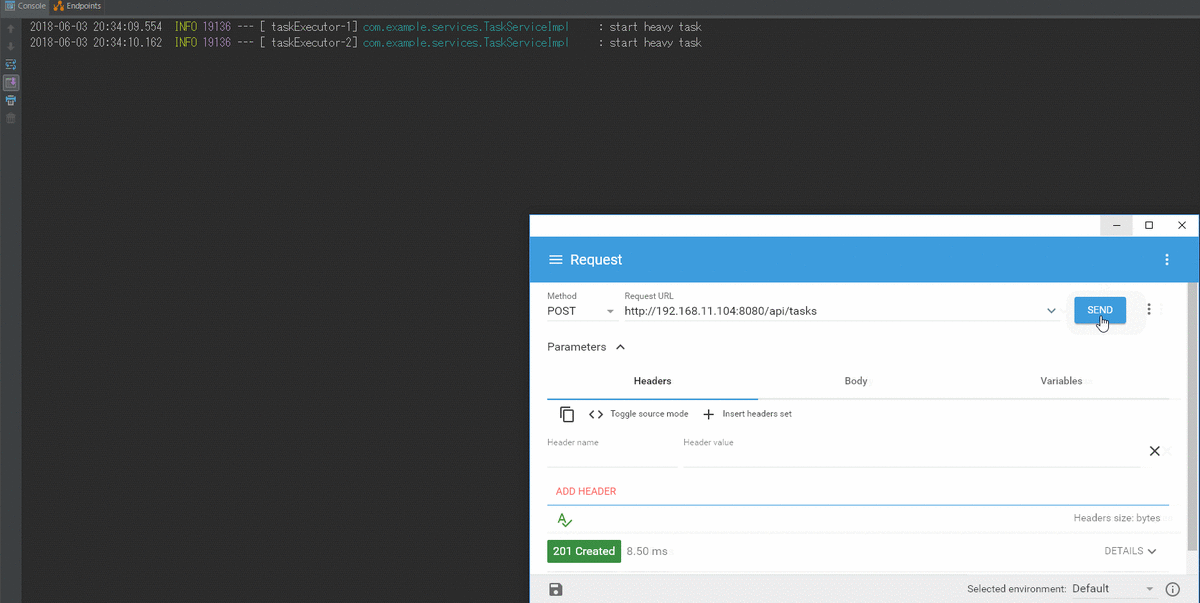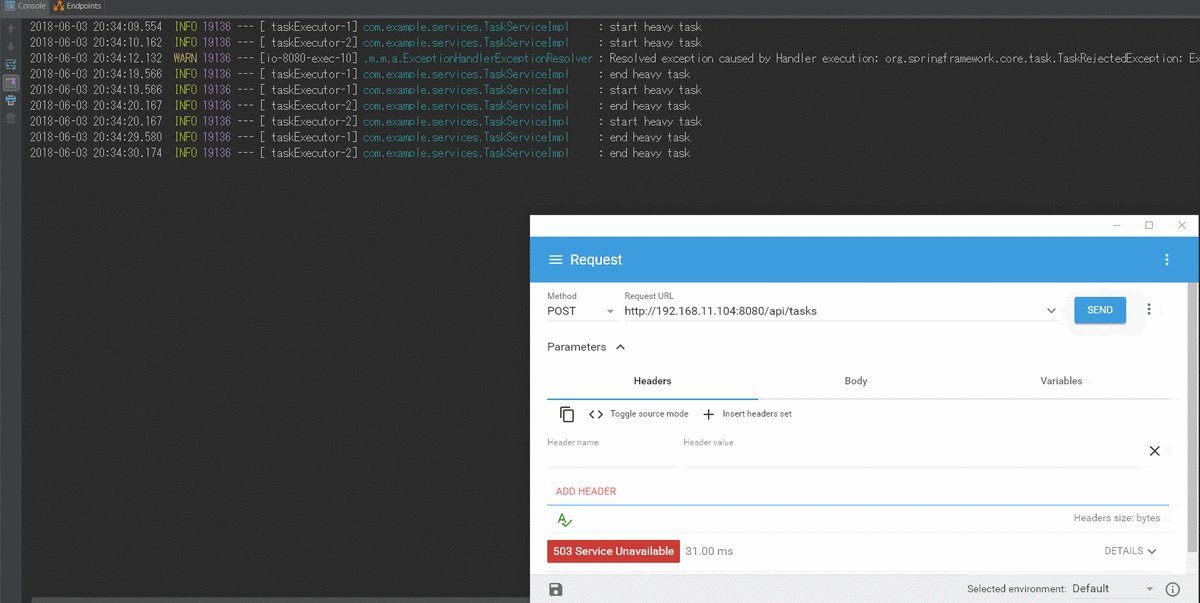
スレッドのキューサイズを超えた場合はデフォルトだと、TaskRejectedExceptionが発生する。 @ExceptionHandlerで例外をハンドリングする。
@RestController
@AllArgsConstructor
@RequestMapping("api/tasks")
public class TaskRestController {
private final TaskService taskService;
@PostMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public Boolean createNewTask() {
taskService.heavyTask();
return true;
}
@ExceptionHandler(TaskRejectedException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE)
public String handle() {
return "too busy";
}
}
検証結果
- 同時実行がsetMaxPoolSizeで制限できている
- 最大キューサイズがsetQueueCapacityで制限できている
- 最大キューサイズを超えると
ExceptionHandler(TaskRejectedException.class)の処理が呼ばれる